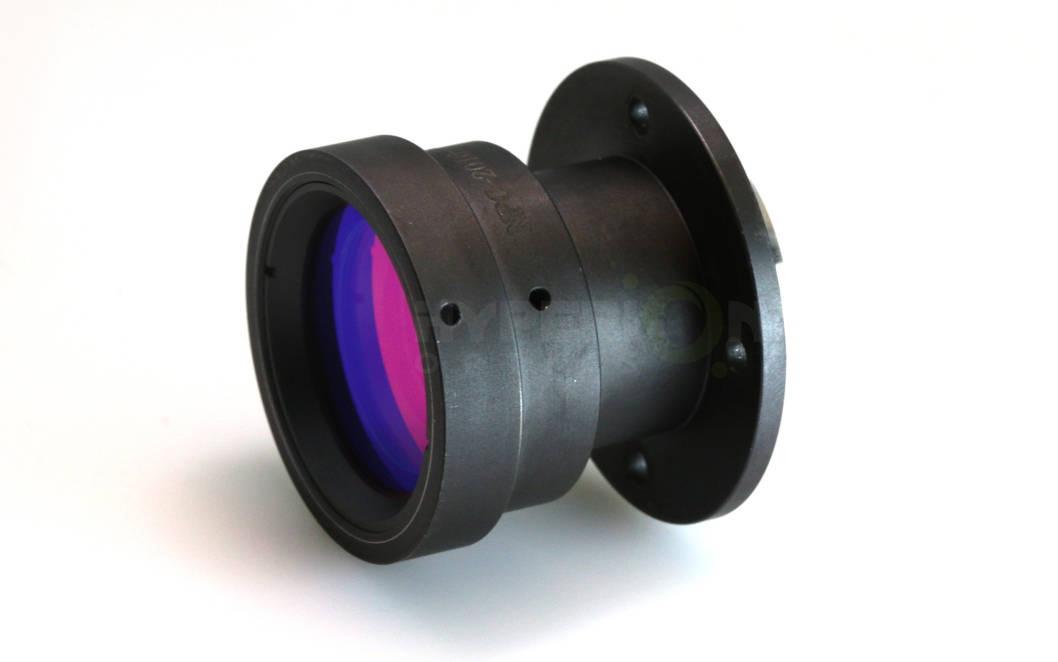

Hyperion's custom collimator lenses help parallelize
the entrance light rays into your optical system setup, enabling you to control
the field of view, collection efficiency, and spatial resolution. Our existing
collimator design is responsive at UV-VIS, or VIS-NIR spectrum.
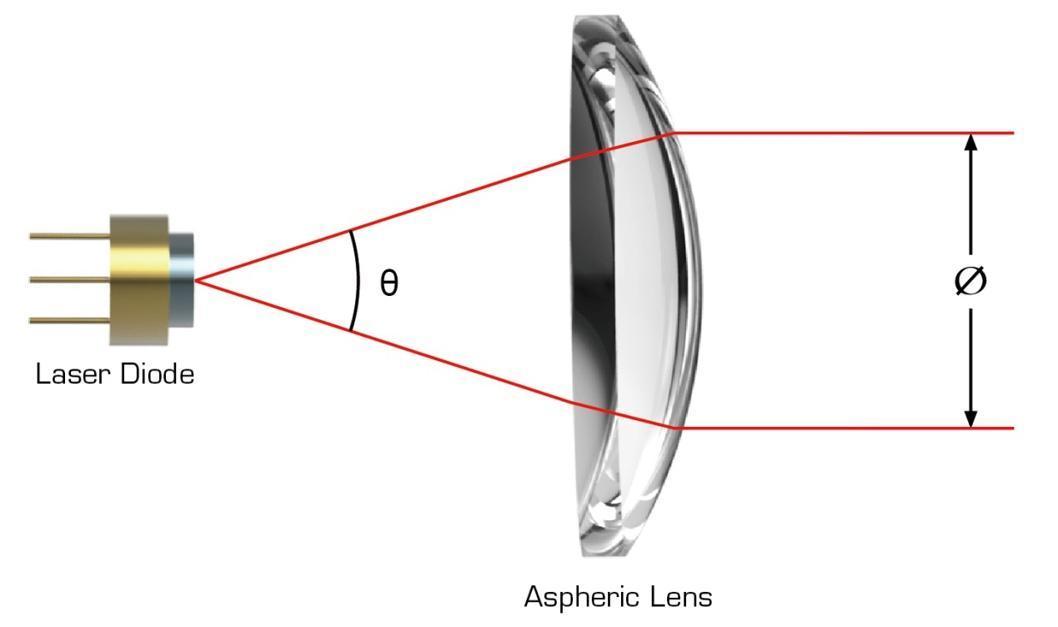
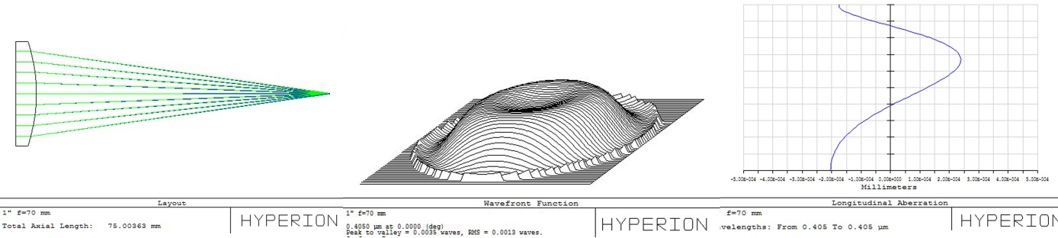
To start with your customized collimating lens design, please verify the expected spot size and focal length of your setup:
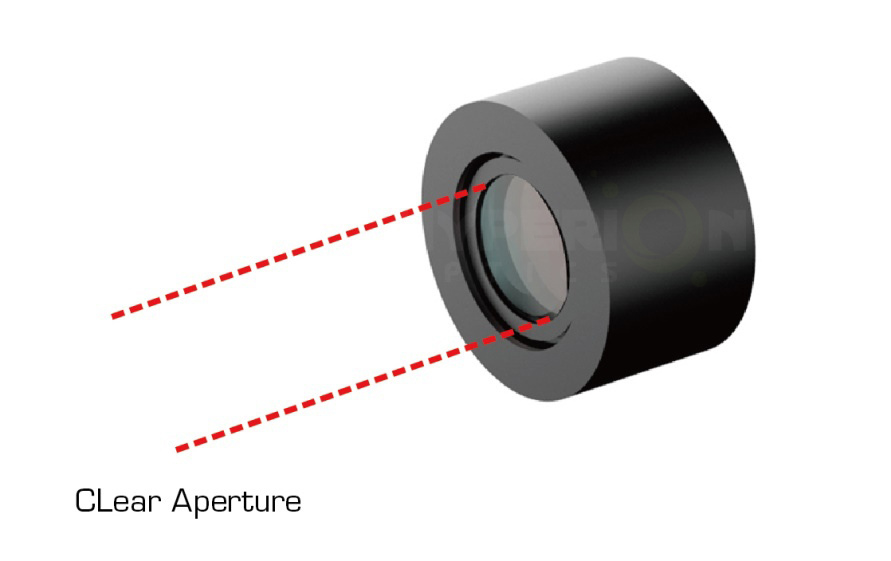
For a point source, near collimation can be assumed so that the beam will be the “clear” aperture of the laser collimating lens. If a fiber is attached to the lens, the divergence angle can be calculated depending on the height of the thread. This information allows you to calculate the spot size at a distance.
Should I choose a chromatic or singlet collimator
lens?
For applications such as absolute
irradiance, the use of achromatic lenses can offer the maximum benefits. An
achromatic lens helps to eliminate the unexpected “contamination” of the
spectrum caused by wavelength outside of the optimal FOV.
Further, Hyperion Optics offers free consultation
on your mechanical design, including lens mount, barrel, and, assembly housing.
Contact our technical sales team today to find out the best collimating
solution for your optical system.
The collimating lens can transform the optical transmission of an optical fiber into a quasi-direct light (parallel light), or parallel (approximate parallel) light to a single mode fiber.
The collimating lenses of the reflector and transmission types are used in the beam transmission system to maintain the quasi-straightness of the beam between the laser resonator and the focusing optical element. The reflection type collimating lens is used in a copper full mirror, while the collimating lens of transmission type is used In zinc selenide lens.
The collimating lens is a common convex lens, where the diverging light enters, and the parallel light emits, and this convex lens acts as a straight line.
1. The lens (mirror) with the appropriate focal length will be selected according to the required girdle radius of the small divergence Angle. The spot is basically the same size as it needs to be.
2. If the collimation lens refers to the alignment of the light, and adjusts the light path, then the near mirror frame is used to adjust the near field aperture and the far mirror frame is used to adjust the far field aperture. If there is a lens focusing, we should think about the relationship of the near field and far field imaging, otherwise, it will be further off.



 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email us:
Email us:  R&D Center: 9B-4F 401,No.1 Qingnian Road Liando U Valley,Yuhua International Wisdom Valley, Nanjing, 210039 China
R&D Center: 9B-4F 401,No.1 Qingnian Road Liando U Valley,Yuhua International Wisdom Valley, Nanjing, 210039 China









 English
English  cn
cn  de
de  es
es  fr
fr 


