
LWIR lens plays a critical role in thermal imaging surveillance applications, beyond night vision capability, critical targets differentiation in poor vision conditions is considered the most practical attribute in homeland security and defense market segmentation.
Compared to the cooled system, which focal plane array detector kept at -70℃ needs cooling support, uncooled cameras are much more affordable. Aside from superior sensitivity of the cooling system, the uncooled system is dominating the market for surveillance and automobile segmentation due to its cost.
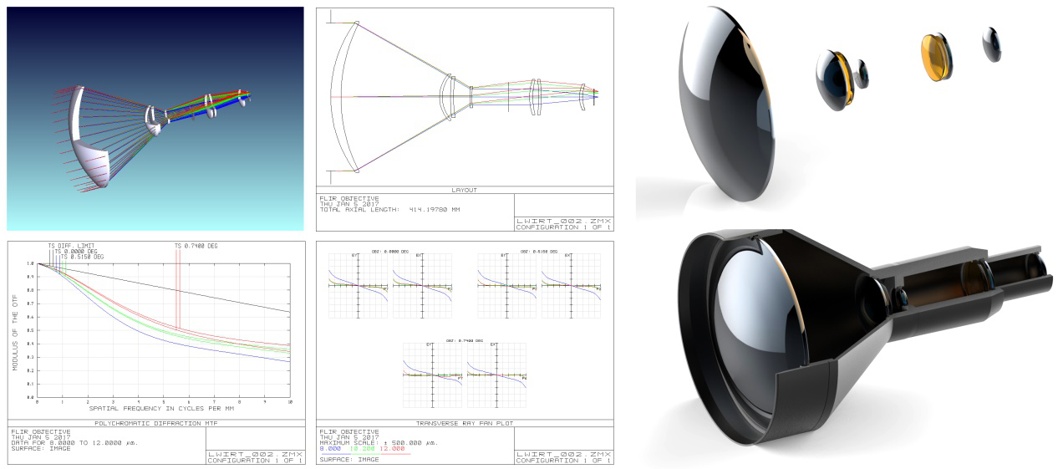
On the other hand, in short distance surveillance applications, the uncooled system is the best choice, but the cameras have to be equipped with objectives that have the larger focal length to maintain resolution. Meanwhile, the F number will increase due to the same entrance aperture, which will dramatically reduce the amount of light for detection. In return, the uncooled system becomes insensitive. Thus, the cost is driven by increasing the aperture (larger lens), eventually, drives uncooled LWIR solution more expensive than cooled version.
Germanium is frequently used for LWIR lenses as its high refractive index in LWIR wave band; However, Germanium has large thermal drift which causes expected defocus with temperature change. Hyperion Optics provides sophisticated design that balance defocus and secure stable performance in consideration of defocusing attributes of the lens, by using ZnSe (8 times better thermal defocusing compare to Germanium)
In LWIR design, Hyperion Optics optical designers also conduct thorough calculation of what happens to the housing with the impact of thermal expansion. Aluminum is frequently used as housing, for example, a 20mm long aluminum housing will increase by 28 microns if the temperature increases for 60℃, the 28-micron change can be considered the same as the LWIR system’s depth of focus.
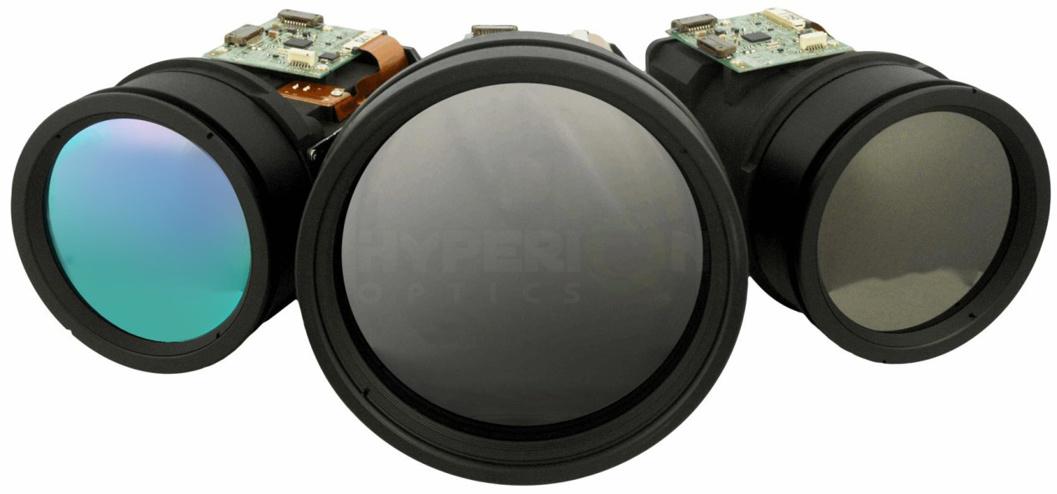

At Hyperion Optics, we conduct both passive mechanical and passive optical solutions for the best to eliminate the thermal impact in thermalization system development. For a passive mechanical solution, we develop inner and outer cell separated by a spacer, geometrically precise machine the spacer with the right material to attain a thermal expansion equal and opposite to the combined effect of the lenses and rest of the housing over the whole temperature range. The spacer pushes the inner cell back to the right position to keep the lens in focus. Find out more by talking or writing to us for your current LWIR needs for our passive optical solution for your own LRIP Optics Project.


Please download the data sheet below:
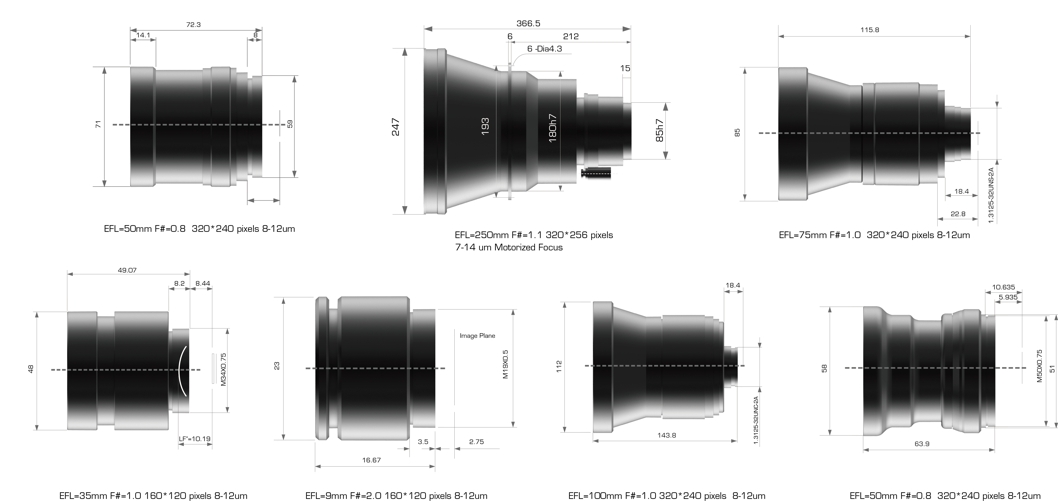
LWIR camera lens is used for thermal imagery. This product provides a high degree of flexibility in frame frequency, user interface and temperature range to make it adapt to various industrial environments and the harsh working environment in the wild. For example, the camera can be adjusted to the optimum condition according to the environment. The adaptability of mechanics, environment and high and low temperature could meet the requirements of military standards. All the functions of the camera, including four different display modes, could achieve the best through the user settings. LWIR Lenses are suitable for infrared detector 320x240, and thermal compensation trimmer is designed completely waterproof.
Special optical glass materials, special coating, and materials.
It can transform focal length in a certain range to get a different angle of view, different sizes of scenes and different scenery range of camera lens. Zoom lens can change the range of shooting by altering focal length without changing the shooting distance. So it's very conducive to picture composition. Because a zoom lens can act as several focal lenses. When traveling, it not only reduces the number of photographic equipment, but also saves the time of changing the lens



 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email us:
Email us:  R&D Center: 9B-4F 401,No.1 Qingnian Road Liando U Valley,Yuhua International Wisdom Valley, Nanjing, 210039 China
R&D Center: 9B-4F 401,No.1 Qingnian Road Liando U Valley,Yuhua International Wisdom Valley, Nanjing, 210039 China









 English
English  cn
cn  de
de  es
es  fr
fr 


